Table of Contents
Introduction
Digital data analysis is a complex and multifaceted concept that requires a clear understanding of its foundational terms. To begin, let us define data. According to Peter Checkland, „Data is a set of values or facts that, when organized and interpreted, becomes information.“ In essence, data can be seen as organized knowledge or raw materials awaiting context and processing.
Moving forward, information is the knowledge derived from data—insights communicated or received about something or someone. In other words, data serves as the building blocks of information, offering structured facts that become meaningful in context.
Lastly, we turn to the definition of analysis, which the Oxford English Dictionary describes as „the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts to gain a better understanding of it.“
With these definitions in mind, one could succinctly state that digital data analysis is the systematic process of breaking down, organizing, and interpreting digital data to extract meaningful insights and inform decisions.
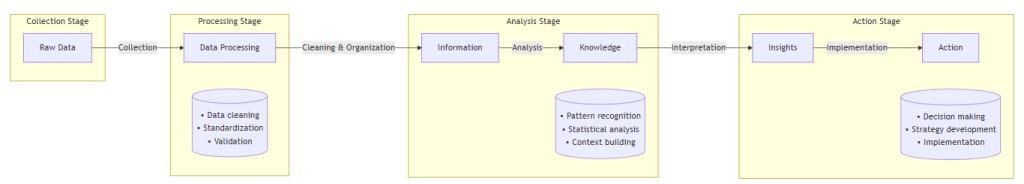
Visual representation of the data-information-analysis process
The Origins and Background of Data Analysis
Data analysis has a rich and fascinating history that dates back to ancient civilizations. Early societies used basic methods of record-keeping to manage resources, monitor populations, and predict agricultural trends. These rudimentary practices laid the groundwork for formal data analysis.
The 17th and 18th centuries marked a turning point with the development of statistical methods. For instance, John Graunt’s analysis of mortality data in London is considered one of the first examples of modern statistical work. These advancements set the stage for governments and organizations to make informed decisions based on data.



Major Incidents in Relation to Data Analysis
Throughout history, significant events have demonstrated the power of data analysis. One notable example is John Snow’s use of data to identify the source of a cholera outbreak in 1854. By mapping cases and analyzing their patterns, he was able to trace the outbreak to a contaminated water pump—saving countless lives and marking a pivotal moment in public health and data analysis.
The 20th century saw data analysis rise to prominence during World War II, where it was used for code-breaking and military strategy. Later, the Space Race highlighted the potential of computers to process vast amounts of data for complex calculations, further cementing the role of data analysis in scientific progress.
The Evolution of Data Analysis
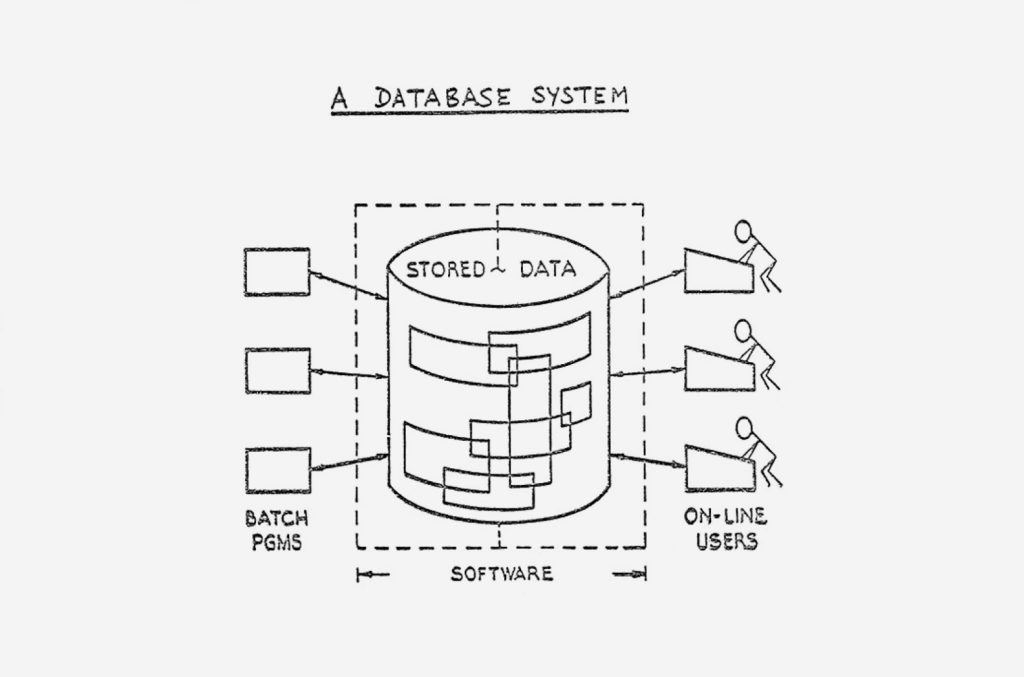
Data analysis has evolved dramatically over the past century. The 1970s introduced relational databases, which revolutionized data storage and retrieval. These systems enabled businesses to organize data efficiently, laying the foundation for modern data warehouses.
With the advent of the internet in the 1990s, data volumes grew exponentially, leading to the era of Big Data. Organizations began adopting advanced analytics tools to process and interpret massive datasets, unlocking new insights.
In the 2000s, machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) started transforming the landscape. Algorithms capable of predictive and prescriptive analytics allowed for more precise forecasting and decision-making. Cloud computing further democratized access to powerful data tools, making analytics accessible to organizations of all sizes. Read more about AI involvement in data analysis
Data Analysis in Today’s World
In today’s digital age, data analysis is a cornerstone of innovation across industries. Businesses use it to optimize operations, predict trends, and improve customer experiences. Governments rely on it for effective policy-making, while healthcare professionals leverage it to advance medical research and improve patient outcomes.
Social media and digital marketing have also transformed data analysis, enabling real-time insights into consumer behavior. Tools like dashboards and interactive visualizations make it easier than ever to explore data and share findings.
The Future of Data Analysis in the Age of AI
The integration of AI is set to redefine data analysis in profound ways. Machine learning algorithms are already automating many tasks, from data cleaning to generating insights. Natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision are expanding the scope of what can be analyzed, enabling machines to interpret unstructured data such as text, images, and videos.
Looking ahead, the rise of autonomous analytics systems may allow machines to identify trends, make predictions, and recommend actions without human intervention. However, this progress also comes with challenges, including concerns about ethics, bias, and data privacy. The future of data analysis will depend on how we balance technological innovation with responsible practices. Explore more about AI and the future of data science

Conclusion
From its humble beginnings in record-keeping to its pivotal role in shaping the future, data analysis has undergone an extraordinary transformation. Today, it powers industries, solves complex problems, and drives innovation. As AI continues to integrate with data analysis, the possibilities are endless—but so too are the responsibilities. By embracing ethical practices, we can ensure that data analysis remains a force for good in an increasingly digital world.
